Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers
1. What is the difference between the terms bandwidth and throughput?
- Bandwidth measures data transfer of web applications and throughput measures data transfer of video applications.
- Bandwidth is measured with Mb/s and throughput is measured in Kbps.
- Bandwidth is the capacity of data transfer in a network and throughput is the actual data transfer rate.
- Bandwidth represents the data transfer rate in a local network and throughput represents the data transfer rate over the Internet.
2. Refer to the exhibit. Which set of devices contains only end devices?
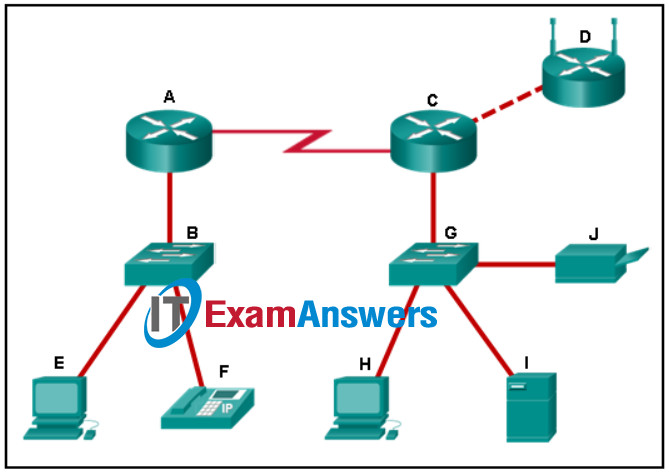
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q2
- B, E, G, H
- E, F, H, I, J
- D, E, F, H, I, J
- A, C, D
- C, D, G, H, I, J
3. Which scenario describes a peer-to-peer network?
- A user visits a webpage on the company web site.
- Users print documents from a network printer that has a built-in NIC.
- Users access shared files from a file server.
- A user has shared a printer attached to the workstation.
4. When a computer assembles a frame to be sent over the network, what is the maximum size of an Ethernet frame?
- 64 bytes
- 1518 bytes
- 128 bytes
- 1024 bytes
5. Refer to the exhibit. The exhibit shows a small switched network and the contents of the MAC address table of the switch. PC1 has sent a frame addressed to PC3. What will the switch do with the frame?
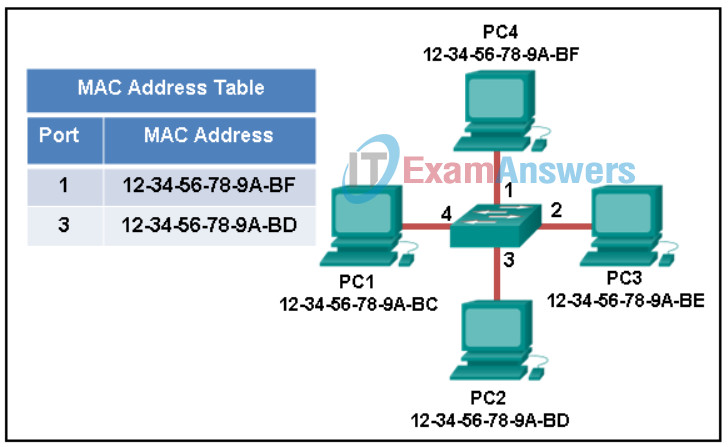
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q5
- The switch will forward the frame only to ports 1 and 3.
- The switch will forward the frame only to port 2.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports except port 4.
- The switch will discard the frame.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports.
6. What is the function of ARP?
- resolves domain names to IP addresses
- sends error and operational information messages to hosts
- provides automatic IP address assignments to hosts
- maps IPv4 addresses to MAC addresses
7. Users are complaining that they are unable to browse certain websites on the Internet. An administrator can successfully ping a web server via its IP address, but cannot browse to the domain name of the website. Which troubleshooting tool would be most useful in determining where the problem is?
- nslookup
- netstat
- ipconfig
- tracert
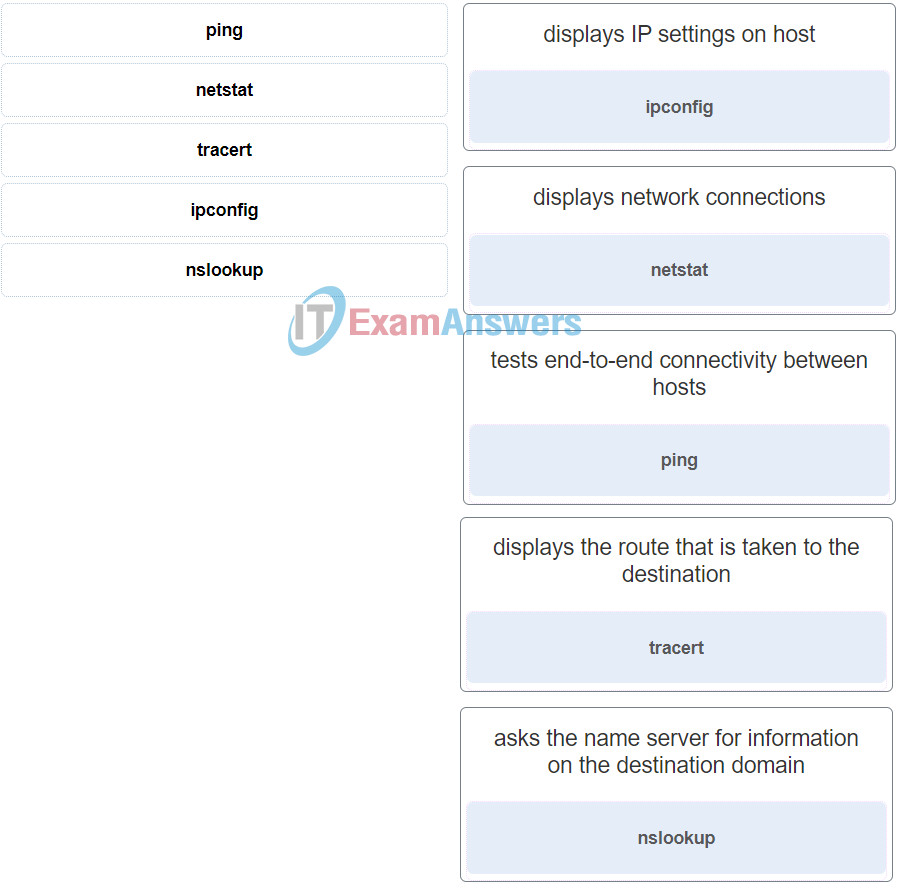
8. Match the command to the function.
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q8
9. A medium-sized company uses APs, WLCs, and laptops for employee workstations. An employee reports the inability to connect to the Internet. A technician verifies that other workstations can successfully connect to the Internet. What are two possible reasons for the problem? (Choose two.)
- The AP does not have power.
- The wireless client is not configured for DHCP.
- A bad cable exists between the client and the WLC.
- A default gateway is improperly configured on the AP.
- The workstation is out of range.
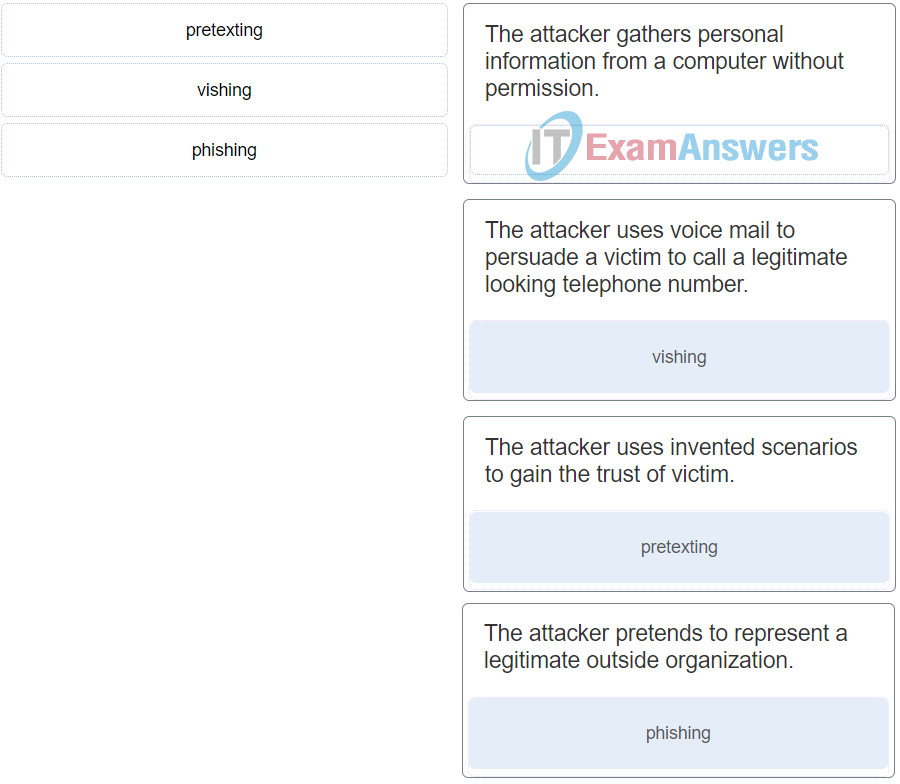
10. Match the type of attack with the description. (Not all options are used.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q10
11. Which three attacks exploit vulnerabilities in software? (Choose three.)
- phishing
- Trojan horses
- worms
- viruses
- vishing
- pretexting
12. A file is downloaded from the Internet. After the user opens the downloaded file, the hard drive crashes and all information on the computer is lost. What type of attack occurred?
- worm
- denial of service
- Trojan horse
- virus
13. What are two ways to protect a computer from malware? (Choose two.)
- Keep software up to date.
- Use antivirus software.
- Empty the browser cache.
- Defragment the hard disk.
- Delete unused software.
14. Which memory location on a Cisco router or switch will lose all content when the device is restarted?
- ROM
- NVRAM
- flash
- RAM
15. Which memory location on a Cisco router or switch stores the startup configuration file?
- ROM
- RAM
- NVRAM
- flash
16. Which network device makes forwarding decisions based on the destination MAC address that is contained in the frame?
- switch
- hub
- router
- repeater
17. A user is looking for a wireless headphone for listening to songs stored on a smartphone. What wireless technology would the headphone use?
- infrared
- Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth
- 3G/4G
18. Which three features represent benefits of virtualization? (Choose three.)
- less device monitoring
- improved disaster recovery
- less employee technical training
- less equipment
- less power consumption
- fewer security requirements
19. A company has a few employees that are designers. The designers do not have the CAD application loaded on their local computer. Instead, the designers use a CAD application hosted by the application developer. Which type of virtualization is the company using?
- DaaS
- PaaS
- SaaS
- IaaS
20. What is the purpose of the startup configuration file on a Cisco router?
- to facilitate the basic operation of the hardware components of a device
- to contain the configuration commands that the router IOS is currently using
- to contain the commands that are used to initially configure a router on startup
- to provide a limited backup version of the IOS, in case the router cannot load the full featured IOS
21. Which two steps are required before SSH can be enabled on a Cisco router? (Choose two.)
- Give the router a host name and domain name.
- Create a banner that will be displayed to users when they connect.
- Set up an authentication server to handle incoming connection requests.
- Enable SSH on the physical interfaces where the incoming connection requests will be received.
- Generate a set of secret keys to be used for encryption and decryption.
22. The global configuration command ip default-gateway 172.16.100.1 is applied to a switch. What is the effect of this command?
- The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
- The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.
- The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
- The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
23. Match the client operation to the network service.
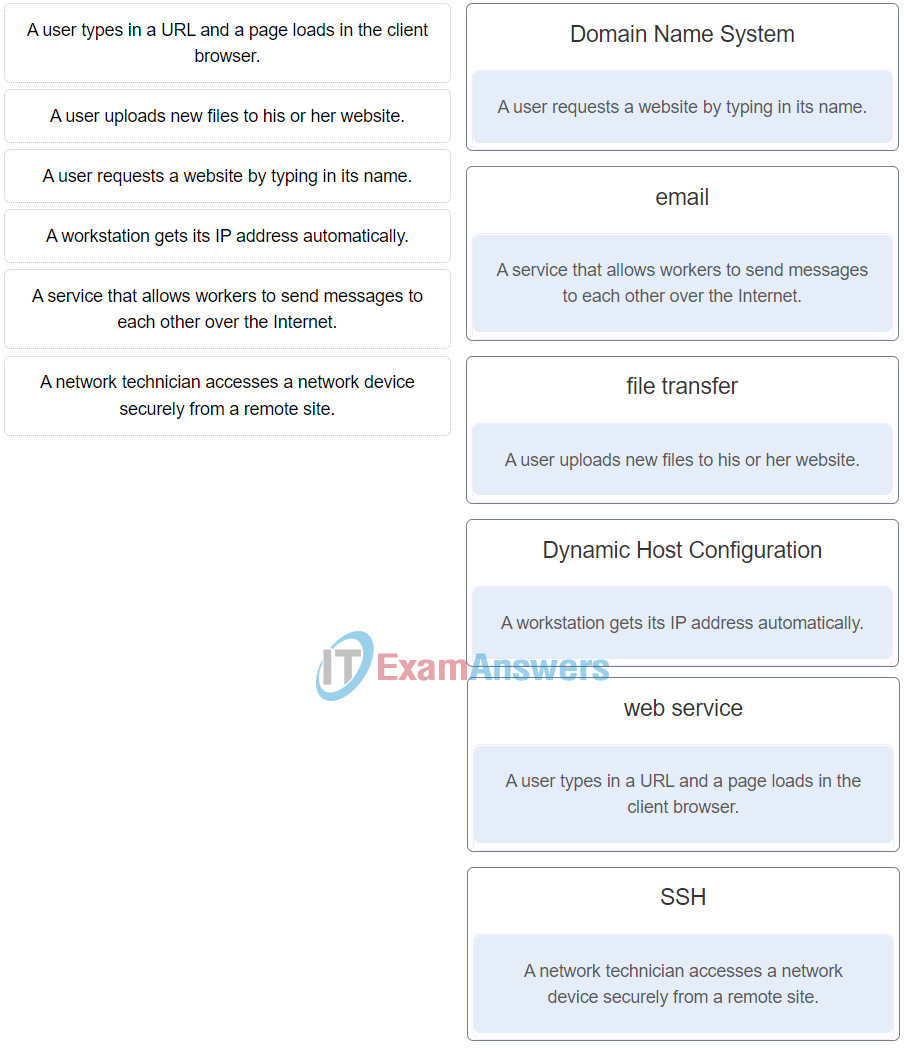
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q23
24. What action does a DNS server take if it does not have an entry for a requested URL?
- The server assigns a temporary IP address to the name and sends this IP address to the client.
- The server returns a “page not found” response to the client.
- The server checks with another DNS server to see if it has an entry.
- The server drops the request.
25. A network security administrator is writing documentation on the firewall requirements for allowing Telnet access to the remote server. Which two pieces of information should be included? (Choose two.)
- port 23
- UDP
- port 22
- TCP
- port 20
26. A new employee is attempting to configure a cell phone to connect to the email server of the company. What is the source port number when sending an email from a mobile device?
- The source port number is 143.
- The source port number is dynamically generated.
- The source port number is 25.
- The source port number is 110.
27. Which function does NAT perform in a wireless router?
- NAT takes an internal source IP address and translates it to a global IP address.
- NAT takes a destination IP address and translates it to a global IP address.
- NAT takes a local IP address and translates it to an internal source IP address.
- NAT takes a source IP address and translates it to a default gateway address.
28. What type of address is automatically assigned to an interface when IPv6 is enabled on that interface?
- link-local
- unique local
- global unicast
- loopback
29. A user is setting up a home wireless network. A global address is to be used in NAT translations for traffic flowing through the wireless router. How is this global address assigned?
- The default gateway IP address of the LAN device is used as the global address for NAT translations through the wireless router.
- The network administrator will choose an available IP address from the LAN and configure the global addressing of the wireless router.
- The wireless router will act as a DHCP client in order to receive global addressing from the ISP.
- The host devices will select an unused IP address on the LAN for performing NAT through the wireless router.
30. A network administrator investigates a user problem. The user can reach hosts on the same network, but is unable to communicate to remote networks.The network administrator tries to ping the gateway address configured on the host device and is unsuccessful. What is the most likely cause of the problem?
- TCP/IP is not installed on the host device.
- The IP address of the user is incorrectly configured.
- The default gateway address is incorrect.
- The address of the remote device is incorrect.
31. Which switch command would a network administrator use to determine if there are encapsulation or media errors on an interface?
- show arp
- show ip interface
- show line
- show interfaces
32. Match the definitions to their respective CLI hot keys and shortcuts. (Not all options are used.)
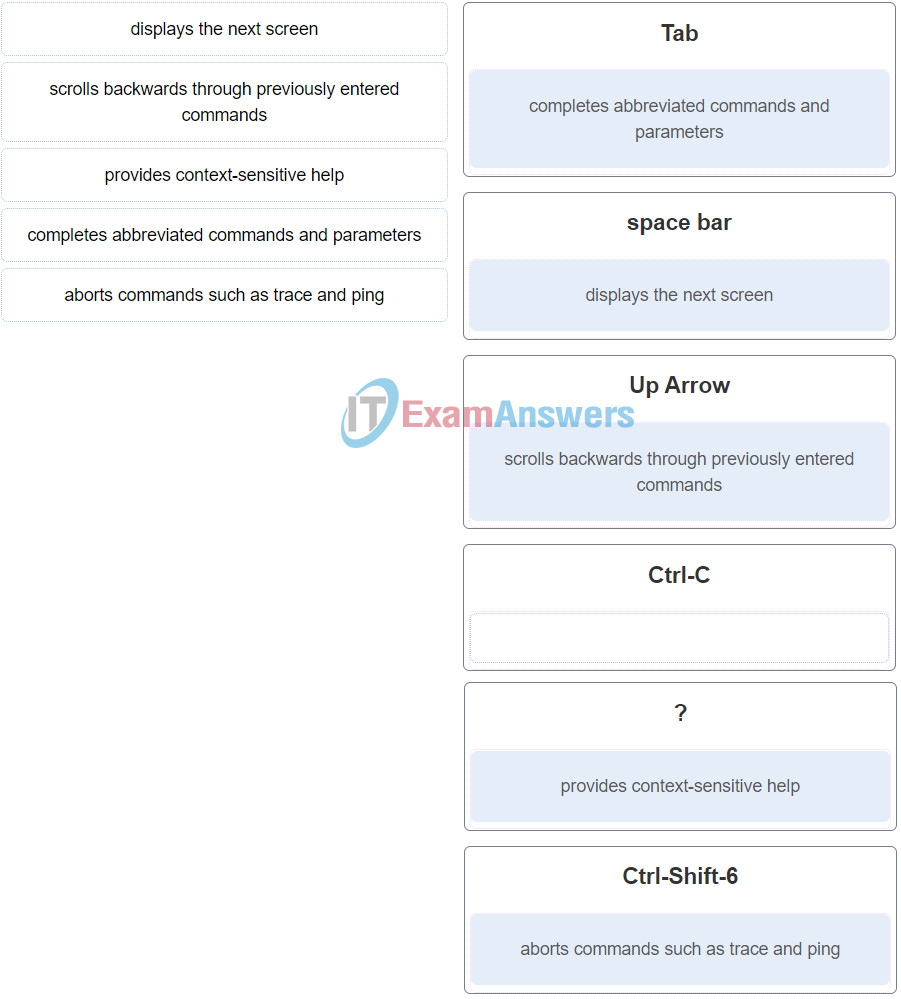
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q32
The shortcuts with their functions are as follows:
– Tab – Completes the remainder of a partially typed command or keyword
– Space bar – displays the next screen
– ? – provides context-sensitive help
– Up Arrow – Allows user to scroll backward through former commands
– Ctrl-C – cancels any command currently being entered and returns directly to privileged EXEC mode
– Ctrl-Shift-6 – Allows the user to interrupt an IOS process such as ping or traceroute
33. Match the description with the associated IOS mode. (Not all options are used.)

Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q33
34. What two default wireless router settings can affect network security? (Choose two.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q34
- The SSID is broadcast.
- MAC address filtering is enabled.
- WEP encryption is enabled.
- The wireless channel is automatically selected.
- A well-known administrator password is set.
35. Which security function is provided by a firewall?
- allows or blocks traffic based on IP address, port number, or application
- passively monitors network traffic and logs intrusion attacks for security analysis
- passively monitors network traffic and automatically blocks intrusion attacks
- aggregates and correlates threat events, contextual information, and network device performance data
36. Which wireless security technology is difficult to crack and provides encryption of network traffic?
- WPA2
- MAC address filtering
- WEP
- EAP
37. When a wireless router is being configured for the first time, what type of wired connection is used?
- modem cable
- console cable
- telephone cable
- Ethernet patch cable
38. Which type of network is covered by the IEEE 802.11 standards?
- Internet
- Wi-Fi
- Ethernet
- WAN
39. Which advanced wireless security measure allows a network administrator to keep sensitive data secure as it travels over the air in a wireless network?
- authentication
- encryption
- MAC address filtering
- traffic filtering
40. Match the TCP/IP model layer to the function.
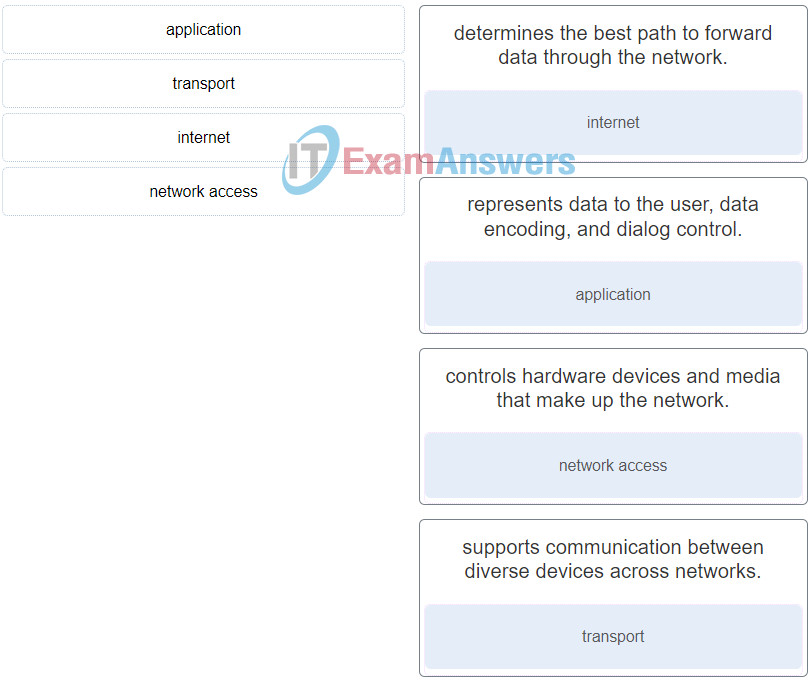
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q40
41. Which three acronyms/initialisms represent standards organizations? (Choose three.)
- TCP/IP
- MAC
- OSI
- IETF
- IEEE
- IANA
42. Which statement is correct about network protocols?
- They are only required for exchange of messages between devices on remote networks.
- They all function in the network access layer of TCP/IP.
- Network protocols define the type of hardware that is used and how it is mounted in racks.
- They define how messages are exchanged between the source and the destination.
43. A company uses DHCP servers to dynamically assign IPv4 addresses to employee workstations. The address lease duration is set as 5 days. An employee returns to the office after an absence of one week. When the employee boots the workstation, it sends a message to obtain an IP address. Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 destination addresses will the message contain?
- MAC address of the DHCP server and 255.255.255.255
- both MAC and IPv4 addresses of the DHCP server
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and IPv4 address of the DHCP server
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and 255.255.255.255
44. When designing an IP address scheme, what is a benefit of using DHCP to assign host addresses?
- Devices on the Internet can easily locate the hosts and send data to them.
- Hosts are permanently assigned an address by the DHCP server so that they are easier to manage
- A gateway address is not required for hosts on one subnet to communicate with hosts on another subnet.
- Changing the subnetting scheme does not require manually reassigning individual host addresses.
45. A network administrator needs to monitor network traffic to and from servers in a data center. Which features of an IP addressing scheme should be applied to these devices?
- dynamic addresses to reduce the probability of duplicate addresses
- predictable static IP addresses for easier identification
- addresses from different subnets for redundancy
- random static addresses to improve security
46. What does the IP address 172.17.4.250/24 represent?
- multicast address
- host address
- broadcast address
- network address
47. What is the decimal equivalent to binary 11110000?
- 192
- 248
- 224
- 240
48. A message is sent to all hosts on a remote network. Which type of message is it?
- unicast
- limited broadcast
- directed broadcast
- multicast
49. A user is attempting to access http://www.cisco.com/ without success. Which two configuration values must be set on the host to allow this access? (Choose two.)
- source MAC address
- DNS server
- default gateway
- source port number
- HTTP server
50. Which three configuration components are required to allow a host to communicate with other hosts on remote networks? (Choose three.)
- IP address
- domain name
- default gateway
- DNS server
- subnet mask
- DHCP server address
51. Which two methods are used to directly connect mobile devices such as tablets and smartphones to a data network? (Choose two.)
- WiMax
- Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth
- cellular communications
- wired Ethernet
52. Why does HTTP use TCP as the transport layer protocol?
- because HTTP requires reliable delivery
- to ensure the fastest possible download speed
- because HTTP is a best-effort protocol
- because transmission errors can be tolerated easily
53. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 needs to resolve the host name of the web server into an IP address by using DNS. What destination IP address and destination port number will PC1 assign to the DNS query packet?
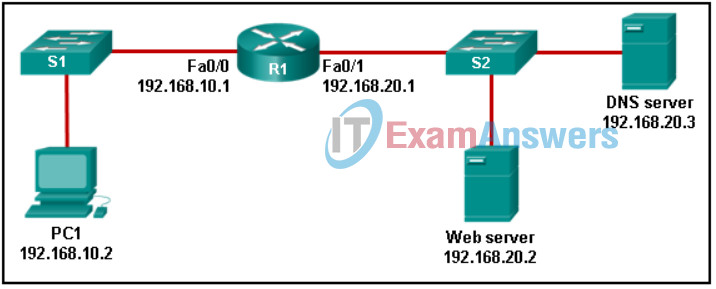
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q53
- 192.168.20.2 port 80
- 192.168.10.1 port 53
- 192.168.20.3 port 53
- 192.168.20.2 port 53
- 192.168.20.3 port 80
54. When is UDP preferred to TCP?
- when all the data must be fully received before any part of it is considered useful
- when segments must arrive in a very specific sequence to be processed successfully
- when a client sends a segment to a server
- when an application can tolerate some loss of data during transmission
55. Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all targets are used.)
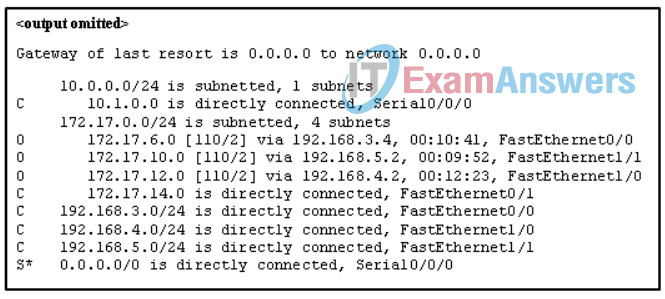
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q55_1
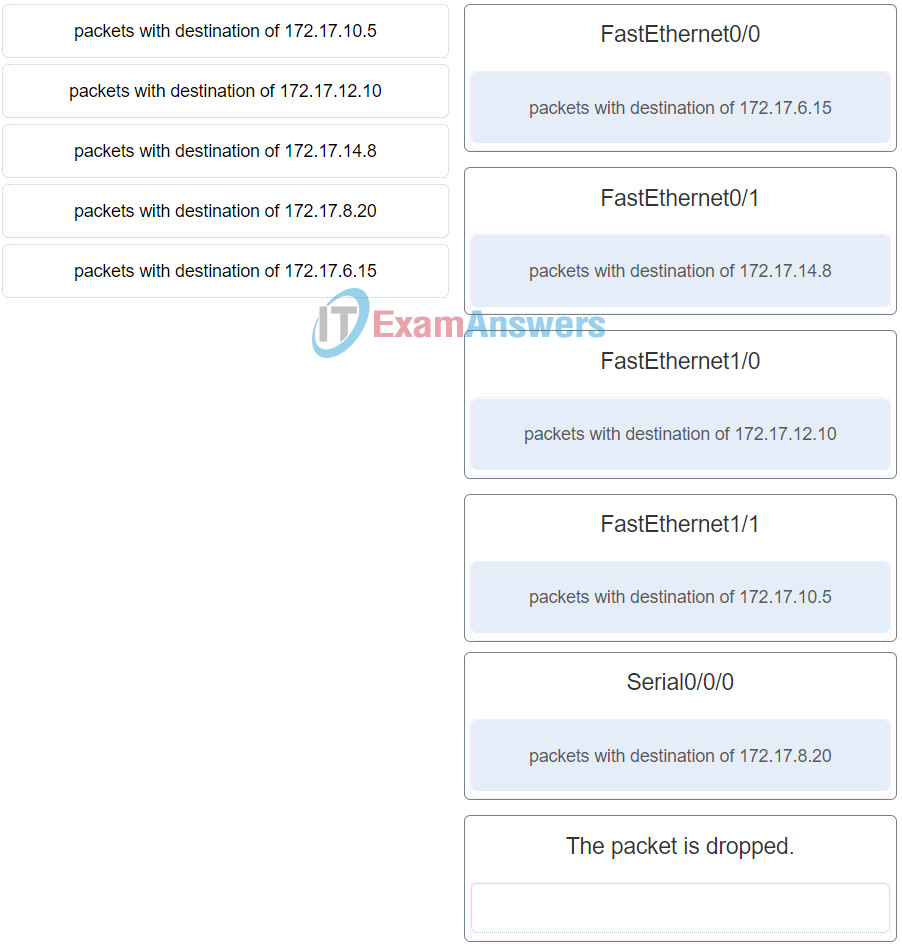
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q55
56. When a router receives a packet, what information must be examined in order for the packet to be forwarded to a remote destination?
- source IP address
- destination IP address
- destination MAC address
- source MAC address
57. A user can access a file share resource on a server located in the same office but cannot access the internet. What is the possible cause?
- The default gateway address is misconfigured on the PC.
- The switch is malfunctioning.
- The DHCP server is disconnected.
- The IPv4 address and subnet mask are misconfigured on the PC.
58. A network technician is extending the network from the main office building over several hundred meters to a new security station. The security station needs a high speed connection to support video surveillance of the main building. What type of cable is best suited to connect the security station to the rest of the main office network?
- fiber optic
- unshielded twisted pair
- shielded twisted pair
- coax
59. What makes fiber preferable to copper cabling for interconnecting buildings? (Choose three.)
- greater bandwidth potential
- easily terminated
- lower installation cost
- durable connections
- limited susceptibility to EMI/RFI
- greater distances per cable run
60. Which statement describes the ping and tracert commands?
- Tracert uses IP addresses; ping does not.
- Tracert shows each hop, while ping shows a destination reply only.
- Both ping and tracert can show results in a graphical display.
- Ping shows whether the transmission is successful; tracert does not.
61. Which three protocols operate at the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- ARP
- POP3
- TCP
- DHCP
- FTP
- UDP
62. Which network design solution will best extend access layer connectivity to host devices?
- implementing EtherChannel
- implementing redundancy
- implementing routing protocols
- implementing wireless connectivity
63. Which network server is malfunctioning if a user can ping the IP address of a web server but cannot ping the web server host name?
- the DHCP server
- the DNS server
- the FTP server
- the HTTP server
64. A PC is not able to connect to a wired network. Pinging the loopback address is successful, but the gateway cannot be reached. On the network switch all the interface lights are on, except for the interface connected to the PC. The LED on the network card is off. What is the most likely cause of this problem?
- The gateway needs to be fixed.
- The network cable is faulty.
- The PC has an incorrect IP address for the DNS server.
- The network switch is faulty.
65. What are two benefits of wireless networks over wired networks? (Choose two.)
- increased security
- anytime, anywhere connectivity
- immunity to interference
- speed
- mobility
66. Which technology is used to uniquely identify a WLAN network?
- MAC address table
- SSID
- WEP
- WPA
67. Match the components in the notation 100Base-T to the specification. (Not all options are used.)
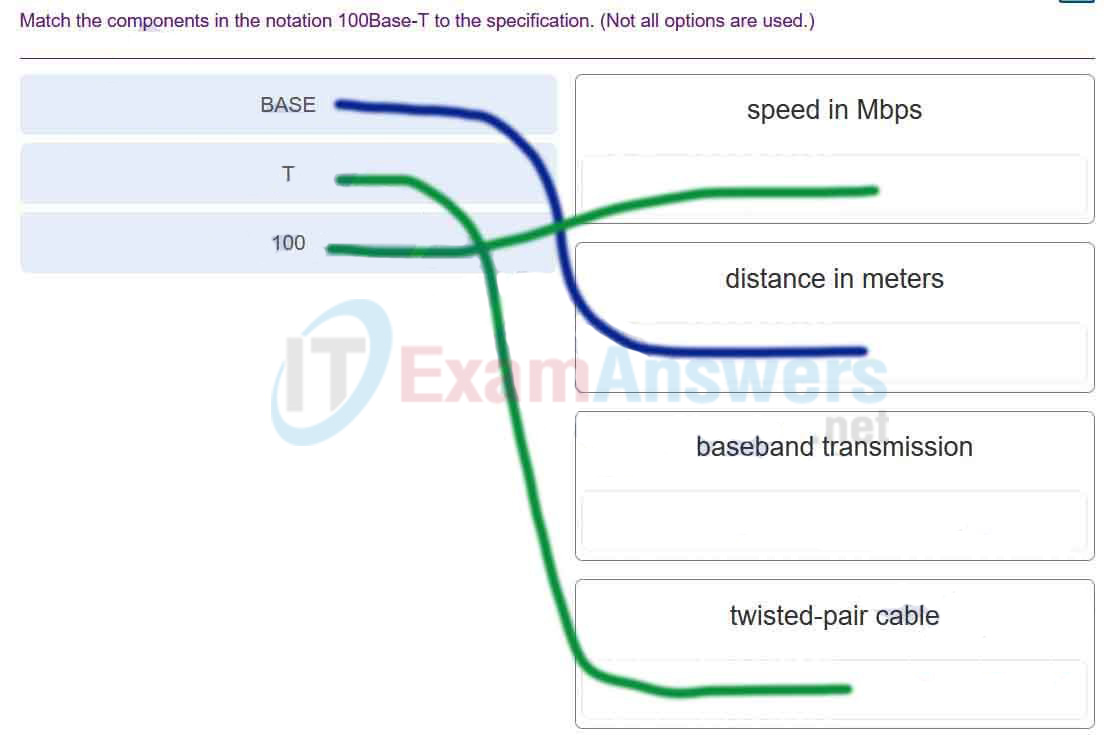
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q67
68. Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as a single layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
- transport
- physical
- network
- data link
- session
69. Which address is a valid IPv6 address that could be assigned to a host?
- 2001:db8::1111::200/80
- 2001:db8::1111::200/64
- 2001:db8:0:1111::200/44
- 2001:db8:0:1111::200/120
70. What does the letter C mean next to an entry in the output of the show ip route command?
- It identifies a network that is a static route.
- It identifies a network that is learned through OSPF.
- It identifies a network that is learned through EIGRP.
- It identifies a network that is directly connected to the router.
71. Which interface allows remote management of a Layer 2 switch?
- the first Ethernet port interface
- the switch virtual interface
- the console port interface
- the AUX interface
72. Which two statements correctly describe the components of a router? (Choose two.)
- ROM contains diagnostics executed on hardware modules.
- Flash memory does not lose its contents during a reboot.
- RAM permanently stores the configuration file used during the boot sequence.
- ROM contains the most current and most complete version of the IOS.
- Flash contains boot system commands to identify the location of the IOS.
- NVRAM stores a backup copy of the IOS used during the boot sequence.
73. Which feature is characteristic of MAC filtering in wireless networks?
- It restricts computer access to a wireless network.
- It encrypts data that is transmitted on a wireless network.
- It allows only authorized users to detect the network.
- It is configured on the computer rather than on the router.
74. Which two statements about a Service Set Identifier (SSID) are true? (Choose two.)
- It is responsible for determining the signal strength.
- It tells a wireless device to which WLAN it belongs.
- All wireless devices on the same WLAN must have the same SSID.
- It provides strong wireless security.
- It is used to encrypt data sent across the wireless network.
75. What are three characteristics of UTP cabling? (Choose three.)
- susceptible to EMI and RFI
- commonly used for Internet connectivity by a cable TV provider
- easiest type of networking cable to install
- commonly used between buildings
- uses light to transmit data
- most commonly used networking cable
76. Which three factors should be considered when choosing the appropriate network media? (Choose three.)
- the data security and fault tolerance requirement
- the environment in which the media is installed
- the amount of data and the data transfer rate desired
- the operating systems used on network devices in the network
- the distance between hosts that the media will connect
- the speed of the CPU and amount of memory in servers
77. What is an advantage of the peer-to-peer network model?
- high level of security
- scalability
- ease of setup
- centralized administration
78. Which three devices are considered intermediate devices in a network? (Choose three.)
- wireless access point
- network printer
- server
- switch
- workstation
- router
79. Which two devices are shared peripherals? (Choose two.)
- touch-pad with digital stylus
- printer
- scanner
- tablet
- laptop
80. Which is a characteristic of a Type 2 hypervisor?
- does not require management console software
- has direct access to server hardware resources
- best suited for enterprise environments
- installs directly on hardware
81. A network administrator attempted to access the company website and received a “page not found” error. The next day the administrator checked the web server logs and noticed that during the same hour that the site failed to load, there was an unusually large number of requests for the website home page. All of the requests originated from the same IP address. Given this information, what might the network administrator conclude?
- The web server was turned off and was not able to service requests.
- It is normal web surfing activity.
- It is likely that someone attempted a DoS attack.
- The link to the website does not have enough capacity and needs to be increased.
82. What technique is used in social engineering attacks?
- sending junk email
- man-in-the-middle
- phishing
- buffer overflow
83. Which three IP addresses are considered private addresses? (Choose three.)
- 192.168.5.29
- 172.17.254.4
- 128.37.255.6
- 198.168.6.18
- 172.68.83.35
- 10.234.2.1
84. Which two application layer protocols manage the exchange of messages between a client with a web browser and a remote web server? (Choose two.)
- HTTPS
- HTML
- DHCP
- HTTP
- DNS
85. Match the port number to the email protocol.
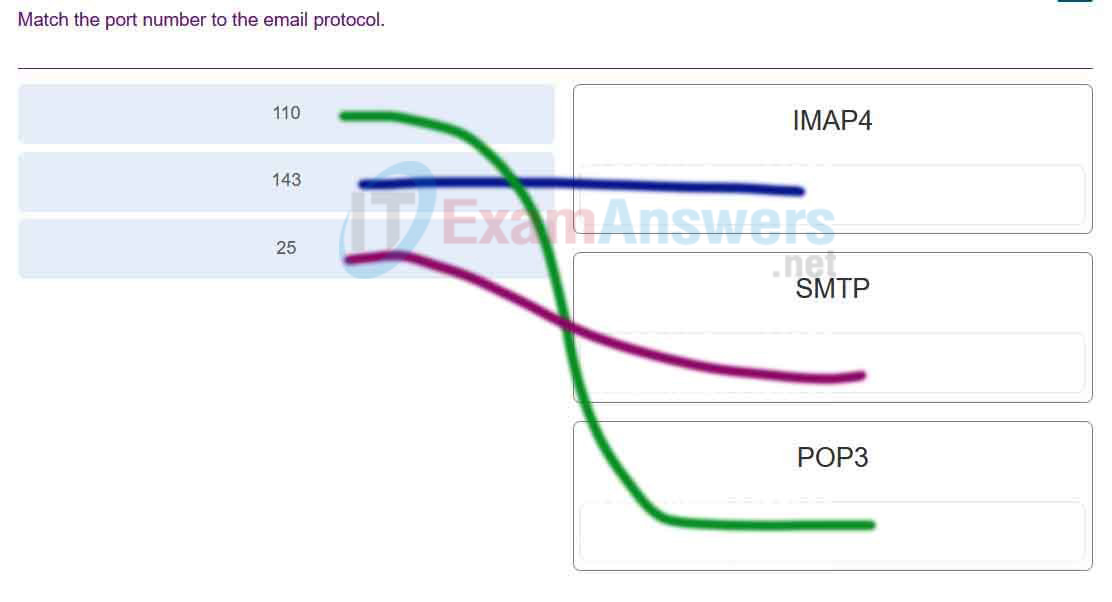
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q85
86. Which protocol is used by a server that needs to send an email message to another server in order to support successful delivery of the message?
- SMTP
- DNS
- POP3
- IMAP4
87. What are two functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- It controls the flow of data via the use of Layer 2 addresses.
- It provides segmentation at Layer 2.
- A router connects multiple IP networks.
- It determines the best path to send packets.
- It builds a routing table based on ARP requests.
88. Which statement describes a major characteristic of a local area network?
- A LAN is under one administrative control.
- A LAN is implemented in a corporation to connect all of its offices.
- A LAN connects remote users to the main corporate office.
- A LAN can contain up to 100 hosts.
89. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator for a small advertising company has chosen to use the 192.168.5.96/27 network for internal LAN addressing. As shown in the exhibit, a static IP address is assigned to the company web server. However, the web server cannot access the Internet. The administrator verifies that local workstations with IP addresses that are assigned by a DHCP server can access the Internet, and the web server is able to ping local workstations. Which component is incorrectly configured?
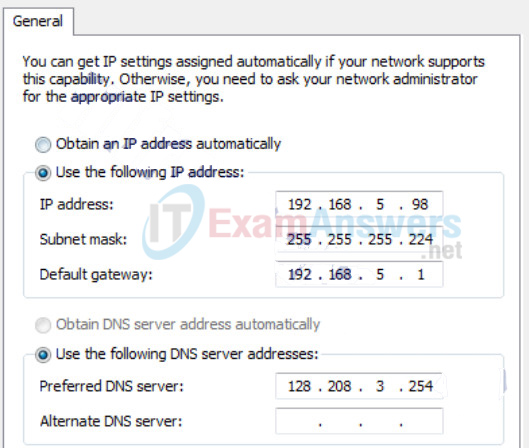
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q89
- subnet mask
- DNS address
- host IP address
- default gateway address
90. A law firm uses DHCPv4 to dynamically assign IPv4 addresses for staff workstations. The DHCP policy specifies that the lease period is 7 days. A staff member returns to the office after 2 weeks of vacation. When the employee turns on the workstation, which DHCPv4 message is sent by the workstation to obtain a valid IPv4 address?
- DHCPACK broadcast message
- DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message
- DHCPOFFER unicast message
- DHCPREQUEST unicast message
91. Match the command with the device mode at which the command is entered. (Not all options are used.)
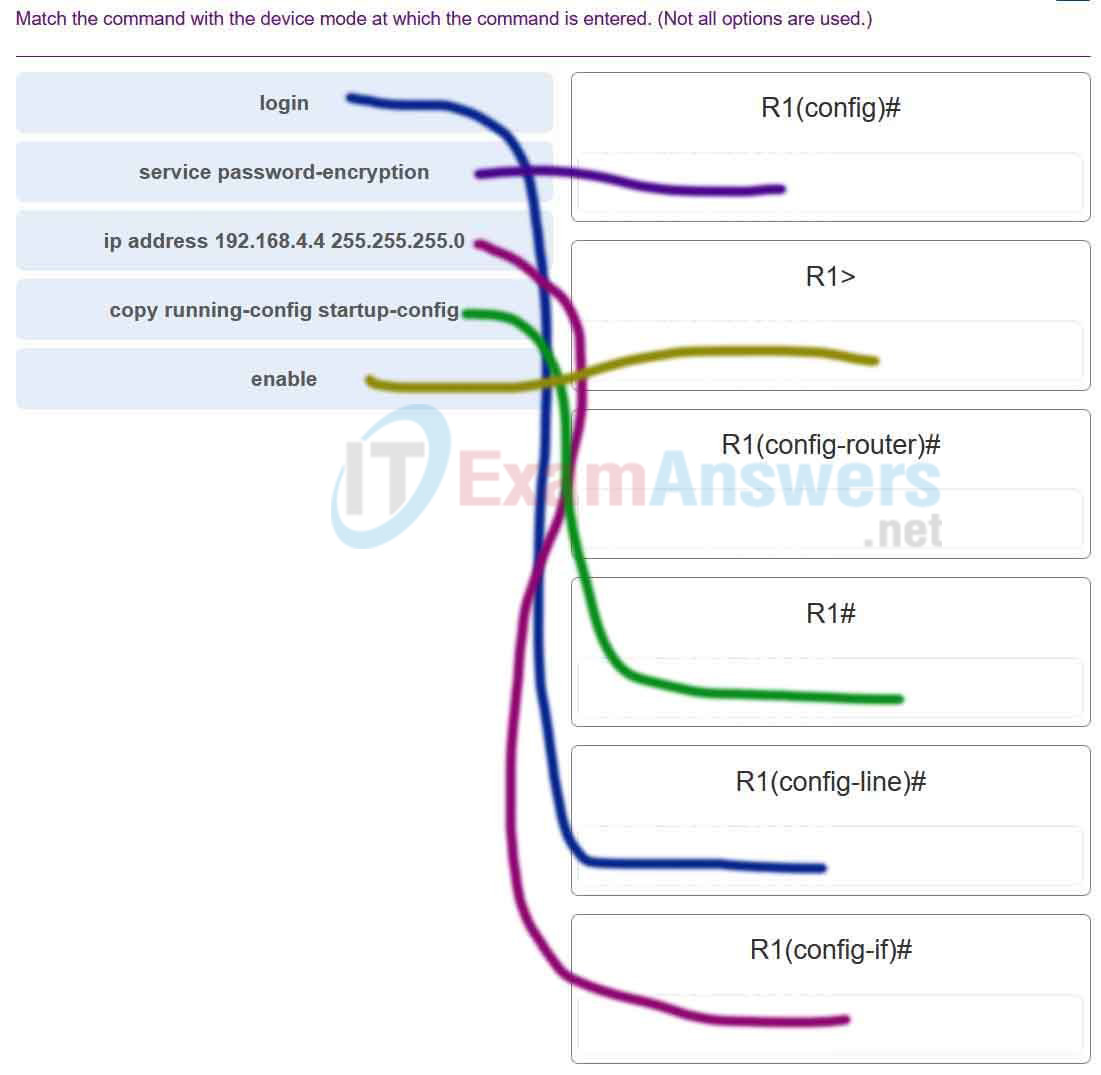
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q91
92. Which three layers of the OSI model make up the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- presentation
- transport
- application
- network
- session
- data link
93. What are two characteristics of 802.11 wireless networks? (Choose two.)
- Stations can transmit at any time.
- They use CSMA/CA technology.
- They are collision-free networks.
- They use CSMA/CD technology.
- Collisions can exist in the networks.
94. Which function is supplied by the access layer in a three-layer network design?
- application of policies
- backbone connectivity
- routing
- network access
- high-speed connectivity
95. When a LAN is connected to the internet using a wireless router, how do devices on the LAN communicate on the internet using NAT?
- Each LAN must select a single client device from the wireless router settings that can communicate to the internet via NAT.
- Only a small group of high priority client devices can be chosen by the wireless router to communicate to the internet using NAT.
- Each device must wait to receive a token from the wireless router in order to communicate to the internet via NAT.
- All devices must share the single public IPv4 address assigned to the wireless router in order to communicate to the internet via NAT.
96. In what situation would a Layer 2 switch have an IP address configured?
- when the Layer 2 switch is the default gateway of user traffic
- when the Layer 2 switch is using a routed port
- when the Layer 2 switch needs to forward user traffic to another device
- when the Layer 2 switch needs to be remotely managed
97. When would the Cisco IOS image held in ROM be used to boot the router?
- when the full IOS cannot be found
- during a normal boot process
- when the running configuration directs the router to do this
- during a file transfer operation
98. A technician has been asked to troubleshoot a simple network problem that seems to be caused by software. Which troubleshooting approach should be used?
- divide and conquer
- bottom-up
- top-down
- substitution
99. A router with a valid operating system contains a configuration file stored in NVRAM. The configuration file has an enable secret password but no console password. When the router boots up, which mode will display?
- user EXEC mode
- privileged EXEC mode
- setup mode
- global configuration mode
100. Which three features represent benefits of virtualization? (Choose three.)
- fewer security requirements
- less power consumption
- improved disaster recovery
- less equipment
- less device monitoring
- less employee technical training
101. What is a difference between the functions of Cloud computing and virtualization?
- Cloud computing utilizes data center technology whereas virtualization is not used in data centers.
- Cloud computing provides services on web-based access whereas virtualization provides services on data access through virtualized
- Internet connections.
- Cloud computing separates the application from the hardware whereas virtualization separates the OS from the underlying hardware.
- Cloud computing requires hypervisor technology whereas virtualization is a fault tolerance technology.
102. Which two types of devices provide dynamic IPv4 addressing for internal hosts on a local network? (Choose two.)
- ISP DHCP server
- PC-based DHCP client
- wireless router
- PC-based DHCP server
- ISP router
103. A technician uses an application to capture packets on the network. One such capture reveals the password that is used by a person in the classroom to initiate a Telnet session with a school network device. What recommendation could the technician make to the person who is using Telnet?
- If possible, enable the network device to use SSH instead of Telnet.
- If possible, configure the business firewall to filter port 23.
- If possible, encrypt the Telnet password on the classroom computer.
- If possible, use a VPN tunnel from the classroom computer to the network device.
104. What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
105. A technician is tasked with connecting a printer directly to the network and making it accessible to all staff in the general vicinity. What type of network cable is most likely used to connect the printer?
- RJ-11
- fiber-optic
- coaxial
- twisted-pair
106. What benefit does DHCP provide to a network?
- DHCP allows users to refer to locations by a name rather than an IP address.
- Hosts always have the same IP address and are therefore always reachable.
- Hosts can connect to the network and get an IP address without manual configuration.
- Duplicate addresses cannot occur on a network that issues dynamic addresses using DHCP and has static assignments.
107. What is the first step that a switch performs during the bootup sequence?
- Low-level CPU initialization begins.
- POST is initiated.
- The default IOS image is loaded.
- The boot loader is loaded.
108. A network engineer working at a community building that provides free WiFi is holding an IT conference tomorrow evening. A previous conference with over 100 attendees just ended less than 24 hours ago and the network engineer is concerned about the availability of dynamic addressing. How will the network engineer ensure that there are enough IP addresses for the attendees arriving at the IT conference tomorrow?
- The network engineer will create a new pool of IP addresses and provide a new network subnet and router configuration for the conference.
- The network engineer will manually release each lease created by the conference attendees yesterday and statically assign the incoming devices at the conference.
- The network engineer will disconnect all devices using an IP address from the DHCP server in preparation for the conference.
- The network engineer will verify that the DHCP leasing time is set for a couple of hours.
109. How are port numbers used in the TCP/IP encapsulation process?
- Source port numbers and destination port numbers are not necessary when UDP is the transport layer protocol being used for the communication.
- Destination port numbers are assigned automatically and cannot be changed.
- If multiple conversations occur that are using the same service, the source port number is used to track the separate conversations.
- Source port and destination port numbers are randomly generated.
110. A student is sending files from a phone to a computer across a network. Which layer of the TCP/IP model is responsible for reassembling these messages as they are received on the computer?
- application
- transport
- Internet
- network access
111. Which logical binary operation is used by a network device to determine the network portion of an IPv4 address with a specified subnet mask?
- AND
- OR
- EQUAL
- NOT
112. A router receives an incoming packet and cannot determine where to forward it. What will the router do?
- save it until a usable path is installed
- send it back to the source host
- drop it
- broadcast it to directly attached networks
113. Refer to the exhibit. A TCP segment was sent by PC1 to the web server via port 80. Because of an unexpected network failure, the data was forwarded by R1 but was not received by R2. Which statement is correct about this scenario?
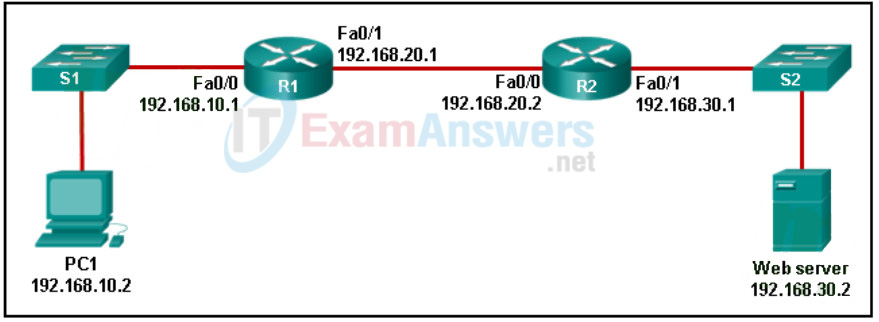
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Q113
- The timer on R1 will expire and R1 will resend the segment to R2.
- R1 will request that PC1 resend the segment.
- The web server will not acknowledge this segment. The PC1 timer will expire and PC1 will resend the segment.
- R1 forwarded the data to R2 but R2 did not receive it. R2 will send a request to R1 to resend the segment.
114. What data representation is used when a computer or network device is processing data?
- binary
- readable
- text
- inferred
115. What command will prevent all unencrypted passwords from displaying in plain text in a configuration file?
- (config)# enable password secret
- (config)# enable secret Encrypted_Password
- (config-line)# password secret
- (config)# enable secret Secret_Password
- (config)# service password-encryption
116. Which statement describes the relationship of a physical network and logical IPv4 addressed networks?
- All devices connected to a physical network need to belong to the same IPv4 logical network.
- A physical network can connect multiple devices of different IPv4 logical networks.
- End devices on different IPv4 logical networks can communicate with each other if they all connect to the same switch.
- A local physical network supports one IPv4 logical network.
117. A DHCP configured PC boots up. What is the order of the messages that are sent and received by this PC in order to obtain an appropriate IP address?
- DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPOFFER, DHCPACK
- DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPOFFER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPACK
- DHCPOFFER, DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPACK
- DHCPREQUEST, DHCPOFFER, DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPACK







