How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank.
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – Modules 21 – 23: Cryptography and Endpoint Protection Group Exam
1. Which type of attack does the use of HMACs protect against?
- brute force
- DDoS
- DoS
- man-in-the-middle
2. Which objective of secure communications is achieved by encrypting data?
- confidentiality
- integrity
- availability
- authentication
3. Which two statements correctly describe certificate classes used in the PKI? (Choose two.)
- A class 4 certificate is for online business transactions between companies.
- A class 0 certificate is more trusted than a class 1 certificate.
- A class 0 certificate is for testing purposes.
- The lower the class number, the more trusted the certificate.
- A class 5 certificate is for users with a focus on verification of email.
4. A customer purchases an item from an e-commerce site. The e-commerce site must maintain proof that the data exchange took place between the site and the customer. Which feature of digital signatures is required?
- nonrepudiation of the transaction
- integrity of digitally signed data
- authenticity of digitally signed data
- confidentiality of the public key
5. What is the purpose of a digital certificate?
- It provides proof that data has a traditional signature attached.
- It guarantees that a website has not been hacked.
- It ensures that the person who is gaining access to a network device is authorized.
- It authenticates a website and establishes a secure connection to exchange confidential data.
6. In a hierarchical CA topology, where can a subordinate CA obtain a certificate for itself?
- from the root CA or another subordinate CA at a higher level
- from the root CA or another subordinate CA at the same level
- from the root CA or from self-generation
- from the root CA only
- from the root CA or another subordinate CA anywhere in the tree
7. What is the purpose for using digital signatures for code signing?
- to establish an encrypted connection to exchange confidential data with a vendor website
- to verify the integrity of executable files downloaded from a vendor website
- to authenticate the identity of the system with a vendor website
- to generate a virtual ID
8. What technology has a function of using trusted third-party protocols to issue credentials that are accepted as an authoritative identity?
- digital signatures
- hashing algorithms
- PKI certificates
- symmetric keys
9. In addressing a risk that has low potential impact and relatively high cost of mitigation or reduction, which strategy will accept the risk and its consequences?
- risk avoidance
- risk reduction
- risk retention
- risk sharing
10. Which two classes of metrics are included in the CVSS Base Metric Group? (Choose two.)
- Confidentiality Requirement
- Modified Base
- Exploit Code Maturity
- Exploitability
- Impact metrics

- develop and implement the appropriate activities to identify the occurrence of a cybersecurity event : detect
- develop and implement the appropriate safeguards to ensure delivery of critical infrastructure services : protect
- develop and implement the appropriate activities to act on a detected cybersecurity event
- develop an organizational understanding to manage cybersecurity risk to systems, assets, data, and capabilities : identify
12. A cybersecurity analyst is performing a CVSS assessment on an attack where a web link was sent to several employees. Once clicked, an internal attack was launched. Which CVSS Base Metric Group Exploitability metric is used to document that the user had to click on the link in order for the attack to occur?
- scope
- integrity requirement
- availability requirement
- user interaction
13. In network security assessments, which type of test employs software to scan internal networks and Internet facing servers for various types of vulnerabilities?
- vulnerability assessment
- risk analysis
- strength of network security testing
- penetration testing
14. What are the three outcomes of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework identify core function? (Choose three.)
- information protection process and procedures
- governance
- mitigation
- risk assessment
- asset management
- recovery planning
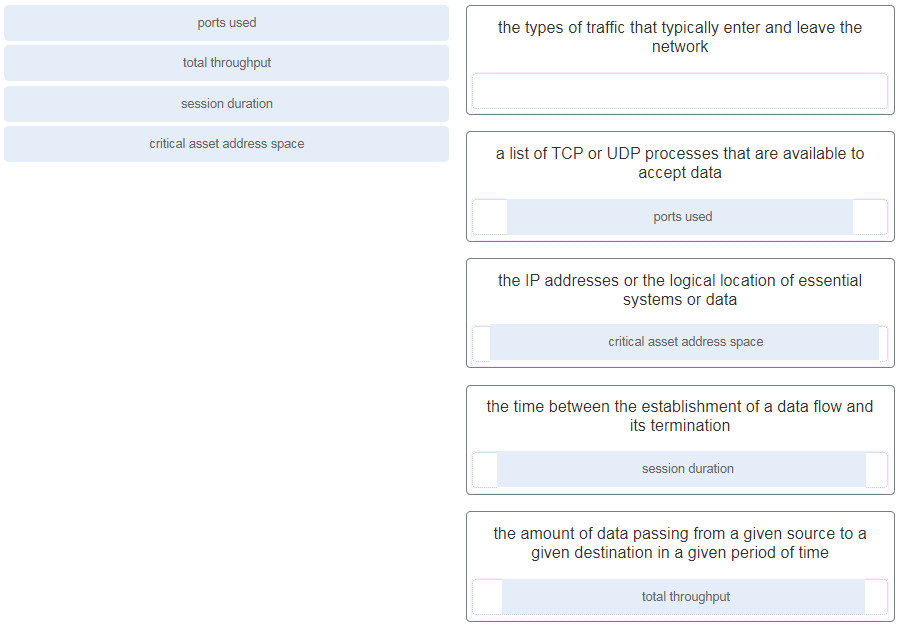
15. When a server profile for an organization is being established, which element describes the TCP and UDP daemons and ports that are allowed to be open on the server?
- critical asset address space
- service accounts
- software environment
- listening ports
16. What is an action that should be taken in the discovery step of the vulnerability management life cycle?
- documenting the security plan
- assigning business value to assets
- developing a network baseline
- determining a risk profile
17. In what order are the steps in the vulnerability management life cycle conducted?
- discover, assess, prioritize assets, report, remediate, verify
- discover, prioritize assets, assess, remediate, report, verify
- discover, prioritize assets, assess, remediate, verify, report
- discover, prioritize assets, assess, report, remediate, verify
17. What does the telemetry function provide in host-based security software?
- It updates the heuristic antivirus signature database.
- It blocks the passage of zero-day attacks.
- It enables updates of malware signatures.
- It enables host-based security programs to have comprehensive logging functions.
19. A security professional is making recommendations to a company for enhancing endpoint security. Which security endpoint technology would be recommended as an agent-based system to protect hosts against malware?
- IPS
- HIDS
- blacklisting
- baselining
20. What is a feature of distributed firewalls?
- They all use an open sharing standard platform.
- They use only TCP wrappers to configure rule-based access control and logging systems.
- They use only iptables to configure network rules.
- They combine the feature of host-based firewalls with centralized management.
21. An administrator suspects polymorphic malware has successfully entered the network past the HIDS system perimeter. The polymorphic malware is, however, successfully identified and isolated. What must the administrator do to create signatures to prevent the file from entering the network again?
- Execute the polymorphic file in the Cisco Threat Grid Glovebox.
- Run the Cisco Talos security intelligence service.
- Use Cisco AMP to track the trajectory of a file through the network.
- Run a baseline to establish an accepted amount of risk, and the environmental components that contribute to the risk level of the polymorphic malware.
22. On a Windows host, which tool can be used to create and maintain blacklists and whitelists?
- Local Users and Groups
- Group Policy Editor
- Task Manager
- Computer Management
23. What is blacklisting?
- This is an application list that can dictate which user applications are not permitted to run on a computer.
- This is a user list to prevent blacklisted users from accessing a computer.
- This is a network process list to stop a listed process from running on a computer.
- This is a Heuristics-based list to prevent a process from running on a computer.
24. Which technology is used by Cisco Advanced Malware Protection (AMP) in defending and protecting against known and emerging threats?
- network admission control
- network profiling
- website filtering and blacklisting
- threat intelligence
25. Which technique could be used by security personnel to analyze a suspicious file in a safe environment?
- sandboxing
- baselining
- whitelisting
- blacklisting
26. Which statement describes the term iptables?
- It is a file used by a DHCP server to store current active IP addresses.
- It is a rule-based firewall application in Linux.
- It is a DHCP application in Windows.
- It is a DNS daemon in Linux.
27. What is the difference between an HIDS and a firewall?
- An HIDS works like an IPS, whereas a firewall just monitors traffic.
- An HIDS monitors operating systems on host computers and processes file system activity. Firewalls allow or deny traffic between the computer and other systems.
- A firewall performs packet filtering and therefore is limited in effectiveness, whereas an HIDS blocks intrusions.
- An HIDS blocks intrusions, whereas a firewall filters them.
- A firewall allows and denies traffic based on rules and an HIDS monitors network traffic.
28. Which statement describes the Cisco Threat Grid Glovebox?
- It is a network-based IDS/IPS.
- It is a host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS) solution to fight against malware.
- It is a sandbox product for analyzing malware behaviors.
- It is a firewall appliance.
29. Which statement describes the policy-based intrusion detection approach?
- It compares the signatures of incoming traffic to a known intrusion database.
- It compares the operations of a host against well-defined security rules.
- It compares the antimalware definitions to a central repository for the latest updates.
- It compares the behaviors of a host to an established baseline to identify potential intrusion.
30. What is the purpose of the DH algorithm?
- to provide nonrepudiation support
- to generate a shared secret between two hosts that have not communicated before
- to encrypt data traffic after a VPN is established
- to support email data confidentiality
31. What is a difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption algorithms?
- Symmetric encryption algorithms are used to authenticate secure communications. Asymmetric encryption algorithms are used to repudiate messages.
- Symmetric encryption algorithms are used to encrypt data. Asymmetric encryption algorithms are used to decrypt data.
- Symmetric encryption algorithms use pre-shared keys. Asymmetric encryption algorithms use different keys to encrypt and decrypt data.
- Symmetric algorithms are typically hundreds to thousands of times slower than asymmetric algorithms.
32. A company implements a security policy that ensures that a file sent from the headquarters office to the branch office can only be opened with a predetermined code. This code is changed every day. Which two algorithms can be used to achieve this task? (Choose two.)
- HMAC
- MD5
- 3DES
- SHA-1
- AES
33. Which security management plan specifies a component that involves tracking the location and configuration of networked devices and software across an enterprise?
- asset management
- patch management
- vulnerability management
- risk management
34. In addressing an identified risk, which strategy aims to stop performing the activities that create risk?
- risk retention
- risk avoidance
- risk sharing
- risk reduction
35. A company is developing a security policy for secure communication. In the exchange of critical messages between a headquarters office and a branch office, a hash value should only be recalculated with a predetermined code, thus ensuring the validity of data source. Which aspect of secure communications is addressed?
- data integrity
- data confidentiality
- non-repudiation
- origin authentication
37. Which three security services are provided by digital signatures? (Choose three.)
- provides nonrepudiation using HMAC functions
- guarantees data has not changed in transit
- provides data encryption
- authenticates the source
- provides confidentiality of digitally signed data
- authenticates the destination







