How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – Modules 18 – 20: Network Defense Group Exam
1. Why is asset management a critical function of a growing organization against security threats?
- It identifies the ever increasing attack surface to threats.
- It allows for a build of a comprehensive AUP.
- It serves to preserve an audit trail of all new purchases.
- It prevents theft of older assets that are decommissioned.
2. In a defense-in-depth approach, which three options must be identified to effectively defend a network against attacks? (Choose three.)
- total number of devices that attach to the wired and wireless network
- assets that need protection
- vulnerabilities in the system
- location of attacker or attackers
- past security breaches
- threats to assets
3. What is the first line of defense when an organization is using a defense-in-depth approach to network security?
- edge router
- firewall
- proxy server
- IPS
4. What three goals does a BYOD security policy accomplish? (Choose three.)
- identify all malware signatures and synchronize them across corporate databases
- identify which employees can bring their own devices
- identify safeguards to put in place if a device is compromised
- identify and prevent all heuristic virus signatures
- identify a list of websites that users are not permitted to access
- describe the rights to access and activities permitted to security personnel on the device
5. Which two options are security best practices that help mitigate BYOD risks? (Choose two.)
- Use paint that reflects wireless signals and glass that prevents the signals from going outside the building.
- Keep the device OS and software updated.
- Only allow devices that have been approved by the corporate IT team.
- Only turn on Wi-Fi when using the wireless network.
- Decrease the wireless antenna gain level.
- Use wireless MAC address filtering.
6. What is the purpose of mobile device management (MDM) software?
- It is used to create a security policy.
- It is used to implement security policies, setting, and software configurations on mobile devices.
- It is used to identify potential mobile device vulnerabilities.
- It is used by threat actors to penetrate the system.
7. What does the incident handling procedures security policy describe?
- It describes how security incidents are handled.
- It describes the procedure for auditing the network after a cyberattack.
- It describes the procedure for mitigating cyberattacks.
- It describes how to prevent various cyberattacks.
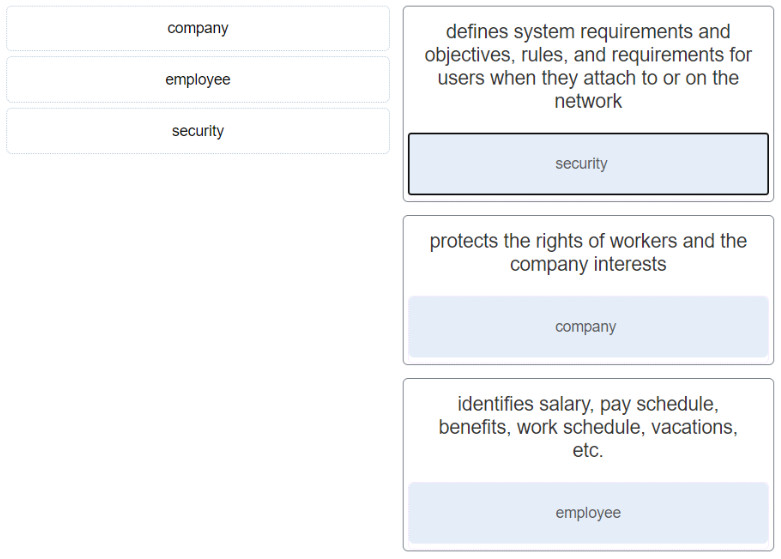
- defines system requirements and objectives, rules, and requirements for users when they attach to or on the network ==> security
- protects the rights of workers and the company interests ==> company
- identifies salary, pay schedule, benefits, work schedule, vacations, etc. ==> employee

- This is the specification for an application layer protocol that allows the communication of CTI over HTTPS. ==> TAXII
- This is a set of specifications for exchanging cyberthreat information between organizations. ==> STIX
- This is is a set of standardized schemata for specifying, capturing, characterizing, and communicating events and properties of network operations. ==> CybOX
10. What is the primary purpose of the Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST)?
- to enable a variety of computer security incident response teams to collaborate, cooperate, and coordinate information sharing, incident prevention, and rapid reaction strategies
- to provide a security news portal that aggregates the latest breaking news pertaining to alerts, exploits, and vulnerabilities
- to offer 24×7 cyberthreat warnings and advisories, vulnerability identification, and mitigation and incident response
- to provide vendor neutral education products and career services to industry professionals worldwide
11. What is the primary purpose of the Malware Information Sharing Platform (MISP) ?
- to publish all informational materials on known and newly discovered cyberthreats
- to enable automated sharing of IOCs between people and machines using the STIX and other exports formats
- to provide a set of standardized schemata for specifying and capturing events and properties of network operations
- to exchange all the response mechanisms to known threats
12. Which statement describes Trusted Automated Exchange of Indicator Information (TAXII)?
- It is a set of specifications for exchanging cyber threat information between organizations.
- It is a signature-less engine utilizing stateful attack analysis to detect zero-day threats.
- It is a dynamic database of real-time vulnerabilities.
- It is the specification for an application layer protocol that allows the communication of CTI over HTTPS.
13. Which organization defines unique CVE Identifiers for publicly known information-security vulnerabilities that make it easier to share data?
- Cisco Talos
- DHS
- FireEye
- MITRE
14. How does FireEye detect and prevent zero-day attacks?
- by establishing an authentication parameter prior to any data exchange
- by addressing all stages of an attack lifecycle with a signature-less engine utilizing stateful attack analysis
- by keeping a detailed analysis of all viruses and malware
- by only accepting encrypted data packets that validate against their configured hash values
15. What is the primary function of the Center for Internet Security (CIS)?
- to maintain a list of common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVE) used by security organizations
- to provide a security news portal that aggregates the latest breaking news pertaining to alerts, exploits, and vulnerabilities
- to offer 24×7 cyberthreat warnings and advisories, vulnerability identification, and mitigation and incident responses
- to provide vendor-neutral education products and career services to industry professionals worldwide
16. What is CybOX?
- It is a specification for an application layer protocol that allows the communication of CTI over HTTPS.
- It is a set of standardized schemata for specifying, capturing, characterizing, and communicating events and properties of network operations.
- It enables the real-time exchange of cyberthreat indicators between the U.S. Federal Government and the private sector.
- It is a catalog of known security threats called Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) for publicly known cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
17. A web server administrator is configuring access settings to require users to authenticate first before accessing certain web pages. Which requirement of information security is addressed through the configuration?
- availability
- integrity
- scalability
- confidentiality
18. When designing a prototype network for a new server farm, a network designer chooses to use redundant links to connect to the rest of the network. Which business goal will be addressed by this choice?
- availability
- manageability
- security
- scalability
19. When a security audit is performed at a company, the auditor reports that new users have access to network resources beyond their normal job roles. Additionally, users who move to different positions retain their prior permissions. What kind of violation is occurring?
- least privilege
- network policy
- password
- audit
20. Which component of the zero trust security model focuses on secure access when an API, a microservice, or a container is accessing a database within an application?
- workflow
- workforce
- workload
- workplace
21. What is the purpose of the network security accounting function?
- to determine which resources a user can access
- to provide challenge and response questions
- to keep track of the actions of a user
- to require users to prove who they are
22. Which term describes the ability of a web server to keep a log of the users who access the server, as well as the length of time they use it?
- authentication
- accounting
- assigning permissions
- authorization
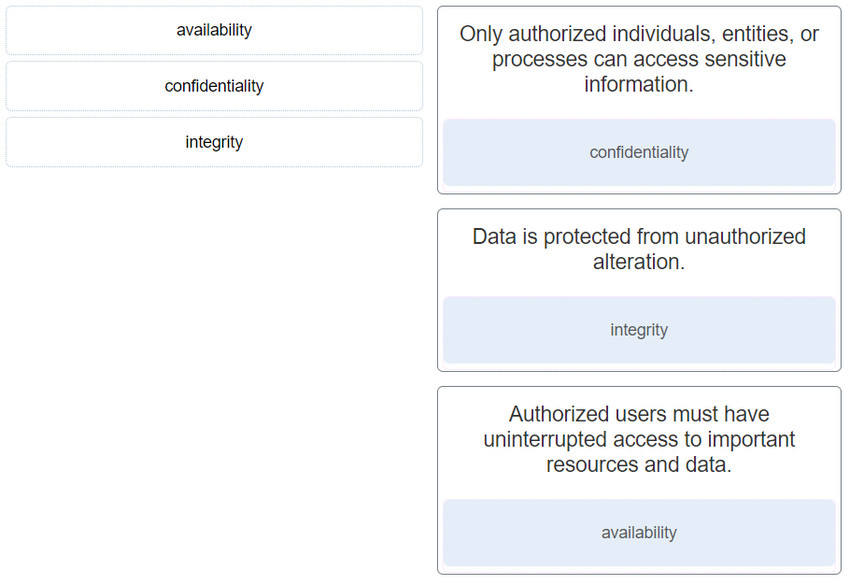
- Only authorized individuals, entities, or processes can access sensitive information. : confidentiality
- Data is protected from unauthorized alteration. : Integrity
- Authorized users must have uninterrupted access to important resources and data. : availability
24. What are two characteristics of the RADIUS protocol? (Choose two.)
- encryption of the entire body of the packet
- encryption of the password only
- the use of UDP ports for authentication and accounting
- the separation of the authentication and authorization processes
- the use of TCP port 49
25. Which AAA component can be established using token cards?
- accounting
- authorization
- authentication
- auditing
26. What is a characteristic of the security artichoke, defense-in-depth approach?
- Threat actors can easily compromise all layers safeguarding the data or systems.
- Threat actors no longer have to peel away each layer before reaching the target data or system.
- Threat actors can no longer penetrate any layers safeguarding the data or system.
- Each layer has to be penetrated before the threat actor can reach the target data or system.
27. What is a characteristic of a layered defense-in-depth security approach?
- Three or more devices are used.
- Routers are replaced with firewalls.
- One safeguard failure does not affect the effectiveness of other safeguards.
- When one device fails, another one takes over.
28. What is the benefit of a defense-in-depth approach?
- All network vulnerabilities are mitigated.
- The need for firewalls is eliminated.
- Only a single layer of security at the network core is required.
- The effectiveness of other security measures is not impacted when a security mechanism fails.
29. Match the term to the description.
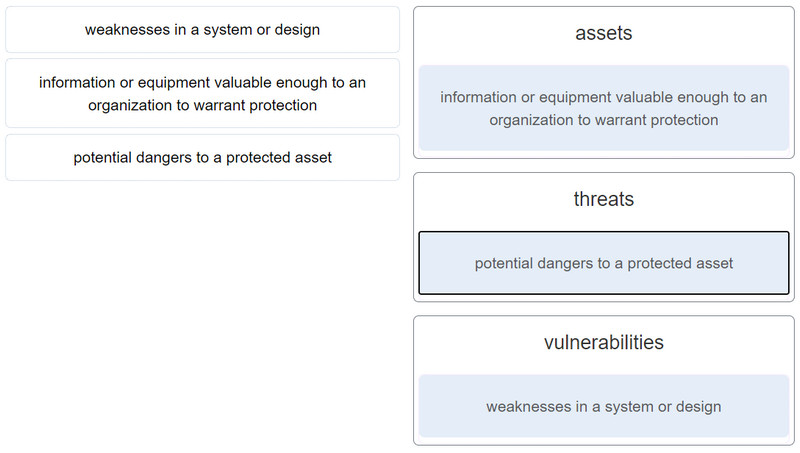
30. What is the principle behind the nondiscretionary access control model?
- It applies the strictest access control possible.
- It allows access decisions to be based on roles and responsibilities of a user within the organization.
- It allows users to control access to their data as owners of that data.
- It allows access based on attributes of the object be to accessed.
31. Which type of access control applies the strictest access control and is commonly used in military or mission critical applications?
- Non-discretionary access control
- discretionary access control (DAC)
- attribute-based access control (ABAC)
- mandatory access control (MAC)
32. Passwords, passphrases, and PINs are examples of which security term?
- identification
- access
- authentication
- authorization
33. How does AIS address a newly discovered threat?
- by creating response strategies against the new threat
- by advising the U.S. Federal Government to publish internal response strategies
- by enabling real-time exchange of cyberthreat indicators with U.S. Federal Government and the private sector
- by mitigating the attack with active response defense mechanisms








SAP C_SACP_2308 Exam Objectives
ReplyDelete