CCNPv8 ENCOR (Version 8.0) – OSPF Exam
1. What is the function of the OSPF LSR packet?
- It is used to confirm the receipt of LSUs.
- It is used to establish and maintain adjacency with other OSPF routers.
- It is used to check the database synchronization between routers.
- It is used by the receiving routers to request more information about any entry in the LSDB.
2. What are two characteristics of OSPF areas? (Choose two.)
- Area 0 is called the backbone area.
- Each OSPF area must be configured with a loopback interface.
- All OSPF areas must be directly connected to Area 0.
- All OSPF networks require the use of multiple areas.
- OSPF areas create a three-layer hierarchical design.
- Single area OSPF networks must be configured in Area 1.
3. Which three requirements are necessary for two OSPFv2 routers to form an adjacency? (Choose three.)
- The OSPF hello or dead timers on each router must match.
- The link interface subnet masks must match.
- The OSPFv2 process ID must be the same on each router.
- The two routers must include the inter-router link network in an OSPFv2 network command.
- The OSPFv2 process is enabled on the interface by entering the ospf process area-id command.
- The link interface on each router must be configured with a link-local address.
4. A network technician issues the following commands when configuring a router:
R1(config)# router ospf 11 R1(config-router)# network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
What does the number 11 represent?
- the OSPF process ID on R1
- the administrative distance that is manually assigned to R1
- the area number where R1 is located
- the autonomous system number to which R1 belongs
- the cost of the link to R1
5. Refer to the exhibit. When OSPF is operational and converged, what neighbor relationship is developed between router R1 and router R2?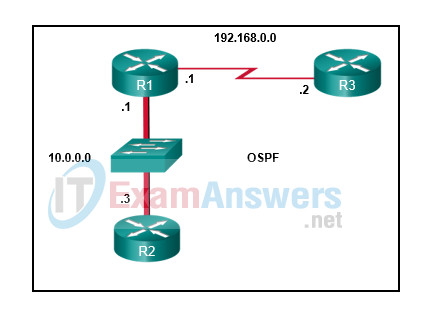
- A FULL adjacency is formed.
- Both routers will become DROTHERS.
- A 2WAY adjacency is formed.
- Router R2 will become the DR and router R1 will become the BDR.
6. Refer to the exhibit. What destination address will RTB use to advertise LSAs?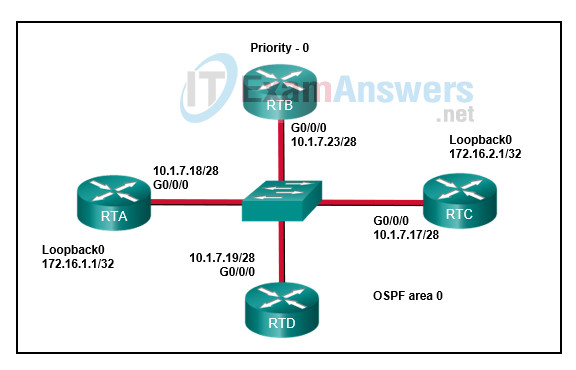
- 10.1.7.17
- 224.0.0.6
- 224.0.0.5
- 255.255.255.255
- 172.16.1.1
- 172.16.2.1
7. A network administrator is implementing OSPF in a portion of the network and must ensure that only specific routes are advertised via OSPF. Which network statement would configure the OSPF process for networks 192.168.4.0, 192.168.5.0, 192.168.6.0, and 192.168.7.0, now located in the backbone area, and inject them into the OSPF domain?
- r1(config-router)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.15.255 area 0
- r1(config-router)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.3.255 area 0
- r1(config-router)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.15.255 area 1
- r1(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 0.0.3.255 area 0
- r1(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 1
- r1(config-router)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.3.255 area 1
8. An administrator is configuring an OSPF router and would like the router to automatically advertise a default route into the OSPF domain even if there is no default route in the RIB. Which configuration will accomplish this?
- default-information originate always
- network 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 area 0
- network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 area 0
- redistribute static
9. Which two variables must match between two OSPF routers to form a neighbor adjacency? (Choose two.)
- K-values
- process IDs
- hello and dead intervals
- area IDs
- router priorities
10. In the planning stages for an OSPF deployment, which step can be taken to reduce router overhead by limiting the size of the link state databases, and LSA Type 1 and Type 2 propagation?
- Use redundant links and alternate paths between routers.
- Increase hello and dead interval timers.
- Ensure that the interfaces of all routers are configured for area 0.
- Divide the OSPF network into multiple areas.
11. Question as presented: Match the OSPF LSA types to their descriptions. (Not all options are used.)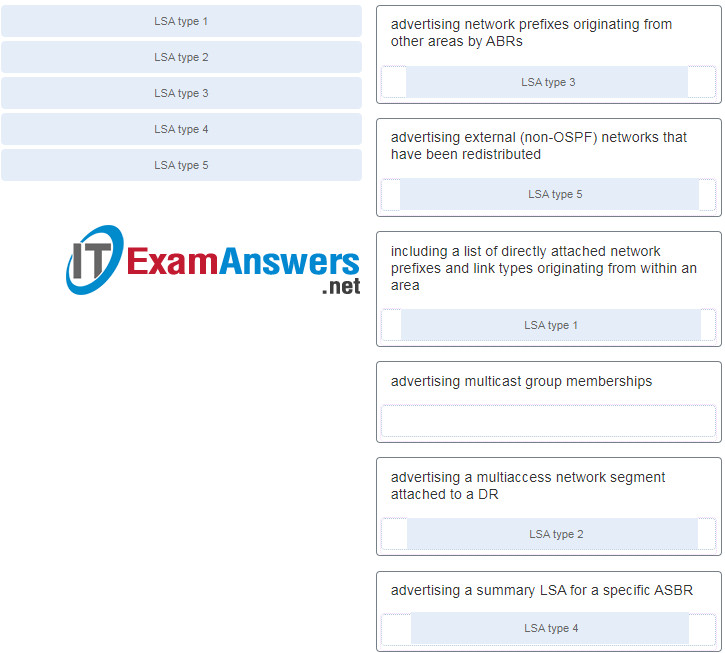
12. Which two statements describe OSPF route summarization? (Choose two.)
- OSPF can perform automatic summarization on major classful network boundaries even if no summarization commands are entered from the CLI.
- Once OSPF route summarization is configured, the summary route will be advertised even if none of the networks in the address range are in the routing table.
- Automatic OSPF route summarization is performed by the ABR.
- The area 51 range 172.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 command identifies area 51 as the area that contains the range of networks to be summarized.
- The metric of the summary route is equal to the lowest cost network within the summary address range.
13. What feature can be configured to filter routes as they are crossing an OSPF ABR?
- distribute list
- prefix list
- summarization
- route map
14. Which LSA type is advertised by all OSPF routers?
- type 1
- type 2
- type 3
- type 4
15. Refer to the exhibit. What can be concluded about network 192.168.1.0 in the R2 routing table?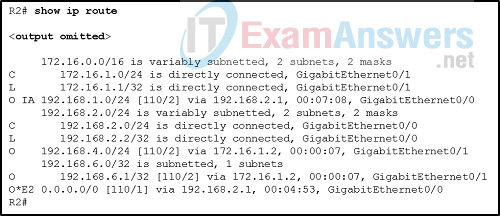
- This network has been learned from an internal router within the same area.
- This network was learned through summary LSAs from an ABR.
- This network is directly connected to the interface GigabitEthernet0/0.
- This network should be used to forward traffic toward external networks.
16. What period of time must elapse before an LSA is purged from the local LSBD if not updated with a new LSA?
- 900 seconds
- 1800 seconds
- 3600 seconds
- 7200 seconds
17. What action does an ABR take when it receives a type 1 LSA?
- it drops the type 1 LSA.
- it floods the type 1 LSA into other nonbackbone areas.
- it creates a type 3 LSA referencing the network in the type 1 LSA and forwards it into other OSPF areas.
- it recreates the type 1 LSA into Area 0.
18. Which LSA type is flooded by a designated router to other OSPF routers within the same area?
- type 1
- type 2
- type 3
- type 4
19. What does an OSPF area contain?
- routers whose SPF trees are identical
- routers that share the same process ID
- routers that have the same link-state information in their LSDBs
- routers that share the same router ID
20. The network administrator has been asked to summarize the routes for a new OSPF area. The networks to be summarized are 172.16.8.0, 172.16.10.0, and 172.16.12.0 with subnet masks of 255.255.255.0 for each network. Which command should the administrator use to forward the summary route for area 15 into area 0?
- area 0 range 172.16.8.0 255.255.248.0
- area 0 range 172.16.8.0 255.255.255.248
- area 15 range 172.16.8.0 255.255.248.0
- area 15 range 172.16.8.0 255.255.255.248
21. Which statement is true about the difference between OSPFv2 and OSPFv3?
- OSPFv3 routers do not need to elect a DR on multiaccess segments.
- OSPFv3 routers use a 128 bit router ID instead of a 32 bit ID.
- OSPFv3 routers use a different metric than OSPFv2 routers use.
- OSPFv3 routers do not need to have matching subnets to form neighbor adjacencies.
22. Which two OSPFv3 LSAs advertise address prefix information? (Choose two.)
- type 1
- type 2
- type 4
- type 8
- type 9
23. Which statement describes the OSPFv3 configuration process?
- The network command is used to enable OSPFv3 on an interface.
- The OSPFv3 router ID is manually configured as a 64-bit value.
- An address family must be initialized before OSPFv3 is enabled on an interface.
- IPv6 routing must be enabled before the OSPFv3 process can start.
24. What IPv6 address does an OSPFv3 router use as the destination address when sending hello packets to discover neighbors?
- FF02::5
- FE80::2
- FF02::6
- FE80::1
25. Which is a difference between OSPFv2 and OSPFv3?
- OSPFv3 uses a 128-bit router ID.
- OSPFv3 and OSPFv2 use different protocol ID numbers.
- OSPFv3 uses different packet types than OSPFv2.
- OSPFv3 does not have built in support for neighbor authentication.
26. How are OSPFv3 routes that are learned from type 1 LSAs identified in the IPv6 routing table?
- O
- EX
- IA
- OI
27. A network administrator enters the command ipv6 router ospf 64 in global configuration mode. What is the result of this command?
- The router will be assigned an autonomous system number of 64.
- The router will be assigned a router ID of 64.
- The OSPFv3 process will be assigned an ID of 64.
- The reference bandwidth will be set to 64 Mb/s.
28. What benefit is provided to OSPFv3 with the two new LSA types, type 8 and type 9?
- They redistribute NSSA LSAs into an area.
- They eliminate SPF calculations when interface addresses are added or changed.
- They permit area routers to locate ASBRs in other areas.
- They advertise default routes learned from other protocols into the OSPFv3 domain.
29. Refer to the exhibit. What two addresses will OSPFv3 neighbors connected to the g0/1 interface of R2 use as the destination address for sending OSPFv3 link-state updates to R2?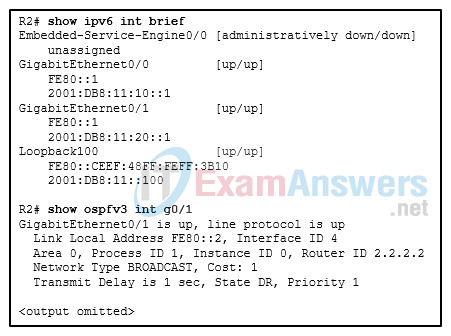
- FF02::5
- FE80::2
- 2001:DB8:11::100
- 2001:DB8:11:20::1
- FF02::6
30. Which type of LSA only exists on networks containing a DR?
- router
- network
- AS external
- summary
31. Which type of LSAs are reduced through interarea summarization?
- type 1 LSAs from all OSPF routers
- type 4 LSAs from ASBRs
- type 3 LSAs from ABRs
- type 2 LSAs from DRs
32. At what level does OSPF maintain a unique LSDB?
- area
- network
- link
- router
33. Refer to the exhibit. Which address will R1 use as the source address for all OSPFv3 messages that will be sent to neighbors?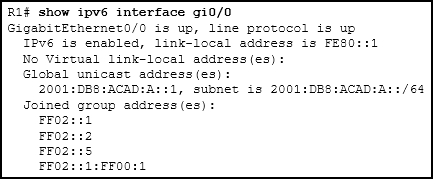
- FF02::1
- 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1
- FE80::1
- FF02::5
34. Which OSPFv3 LSA type is used by ASBRs to announce routes learned through redistribution from other routing protocols?
- type 3
- type 4
- type 5
- type 7







