CCNPv8 ENCOR (Version 8.0) – Wireless Essentials Exam
- The power level of interest is one tenth of the reference value.
- The power level of interest is half the reference value.
- The power level of interest is ten times the reference value.
- The value of the two power levels is the same.
- The power level of interest is double the reference value.
2. While reviewing wireless survey reports, an intern asks a wireless engineer about the term noise floor. What is the definition of noise floor?
- Noise floor is the decreasing of the signal amplitude as it travels through free space.
- Noise floor is the smallest signal strength of the recorded noise received by a receiver.
- Noise floor is the average signal strength of the noise being received by a receiver.
- Noise floor is the maximum signal strength of the recorded noise received by a receiver.
3. Refer to the exhibit. It displays the sources of A, B, and C and the corresponding absolute power of each. In comparing source A and B , how much greater is the signal strength of source B than the signal strength of source A?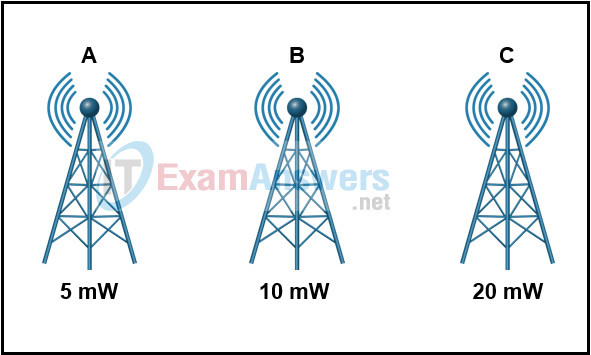
- 3 dB
- 0 dB
- 5 dB
- 10 dB
- 2 dB
4. What is a simple solution to overcome the negative effects of free space path loss?
- increase the cable length of the antenna
- decrease the antenna gain
- increase the transmitter output power
- decrease the transmitter output power
5. What technological factor limits the number of unique spatial streams that can be supported by a MIMO device?
- the number of radios
- the number of transmitters
- the number of receivers
- the processing capacity
6. Which wireless technology allows data to be distributed across two or more radio chains in order to increase data throughput while operating on the same channel?
- narrowband
- direct sequence spread spectrum
- spatial multiplexing
- dynamic rate shifting
7. Which term describes the decrease in signal strength of an RF even though there are no obstacles in the path between a transmitter and a receiver?
- transmit beamforming
- free space path loss
- link budget
- spatial multiplexing
8. How does the 802.11ax amendment (Wi-Fi 6) differ from any other 802.11 wireless standard created before it?
- Wi-Fi 6 can utilize channel widths of 20, 40, 80, or 160 MHz.
- Wi-Fi 6 can support data rates in excess of 150 Mbps per spatial stream.
- Wi-Fi 6 can allow multiple devices simultaneous access to the wireless medium.
- Wi-Fi 6 can support both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz band.
9. Which IEEE standard operates at wireless frequencies in both the 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz ranges?
- 802.11a
- 802.11n
- 802.11b
- 802.11g
10. How does a change in frequency or cycles affect the wavelength of a wireless LAN signal?
- As the number of cycles decreases, the wavelength will increase.
- As the frequency increases, the wavelength will also increase.
- As the frequency decreases, the wavelength will also decrease.
- As the cycles of a wave become larger, the wavelength will cover less distance.
11. An engineer has identified two signals that are 180 degrees out of phase . What can be determined about these two signals?
- These two RF signals will add together as they are received.
- These two RF signals were produced at exactly the same time.
- These two RF signals will tend to cancel each other out as they are received.
- These two RF signals will have matching cycles and identical signals.
12. Which wireless network topology requires that all of the access points be located within a 100 meter radius of an access switch?
- centralized wireless network
- Mobility Express wireless network
- unified wireless network
- embedded wireless network
13. What are two benefits of deploying a centralized wireless LAN topology? (Choose two.)
- decreasing the cable length requirement when utilizing lightweight access points in an embedded wireless network topology
- convenience of enforcing security policies for all wireless users
- lowering the investment cost when utilizing lightweight access points in a Mobility Express topology
- maximizing the number of APs that can join a single WLC
- decreasing the RTT between two wireless clients on a single access point
14. What is a difference between autonomous APs that operate in a home environment and controller-based APs that operate in a corporate environment?
- Autonomous APs do not support PoE.
- Controller-based APs are known as lightweight APs and require an initial configuration to operate.
- Autonomous APs incorporate the functions of a router, switch, and AP into one device.
- Controller-based APs can be automatically configured and managed by a WLAN controller.
15. Which protocol and port number are used when an AP sends a unicast CAPWAP Discovery Request packet to the IP address of a controller? (Choose two.)
- 1645
- UDP
- IP
- 5246
- 1812
- 43
- TCP
16. Which type of topology supports the use of CAPWAP tunnels without the investment of a dedicated wireless LAN controller?
- embedded wireless network
- unified wireless network
- centralized wireless network
- Mobility Express
17. What information is needed by an AP for stateful switchover (SSO) using high availability with a standby WLC?
- the standby WLC
- the group name of the SSO pair
- the IP address of both the primary and standby WLC
- the active primary WLC
18. Why would an AP that successfully discovers a WLAN controller be denied from joining that WLC?
- The name of the WLC is different from the pre-configured name on the Cisco lightweight AP.
- The WLC already has the maximum number of APs joined to it.
- The WLC has a software release downloaded on it that is different from the lightweight AP software.
- The WLC is configured to be the standby WLC in an SSO group.
19. What type of wireless antenna is best suited for providing coverage in large open spaces, such as hallways or large conference rooms?
- directional
- Yagi
- omnidirectional
- dish
20. A wireless engineer accesses the WLC and configures a lightweight access point to function as a sniffer. Which two functions will be performed by the lightweight access point in this mode? (Choose two.)
- The lightweight AP will forward captured traffic to a PC running network analyzer software.
- The lightweight AP will check for IDS events and determine the position of stations through location-based services.
- The lightweight AP will dedicate all of the physical radios to receiving 802.11 traffic from other sources.
- The lightweight AP will correlate MAC addresses heard on the wired network with those heard over the air to detect rogue devices.
- The lightweight AP will offer one or more functioning BSSs on a specific channel.
21. How is the beamwidth of a wireless antenna measured on a plot?
- The beamwidth is determined by finding the weakest point on the plot and following it in either direction until the signal increases by 3 dB.
- The beamwidth is determined by finding the weakest point on the plot and following it in either direction until the signal decreases by 10 dB.
- The beamwidth is determined by finding the strongest point on the plot and following it in either direction until the signal decreases by 3 dB.
- The beamwidth is determined by finding the strongest point on the plot and following it in either direction until the signal decreases by 10 dB.
22. A wireless engineer is troubleshooting signal degradation between two wireless antennas connecting over a distance. If no physical obstructions are found to be blocking the wireless signal, what is most likely the issue?
- The polarization of the transmitting antenna does not match the polarization of the receiving antenna.
- The gain of the transmitting antenna does not match the gain of the receiving antenna.
- The transmitting and receiving antennas are mismatched and not providing a compatible radiation pattern.
- The polarization of the transmitting antenna is 3 dB less than the receiving antenna.
23. What is the purpose of a wireless client sending a reassociation request to an AP?
- to respond to the beacon signal sent by the AP
- to roam from current AP to another AP
- to form a new association with the AP
- to find the SSID of the AP
24. For its customers, a shopping center is deploying a wireless network that consists of 20 lightweight APs that are bound to a single WLC. Which type of roaming occurs when clients roam between APs on the shopping center network?
- intercontroller roaming
- Layer 2 roaming
- autonomous roaming
- intracontroller roaming
25. A company deploys a Cisco wireless network over a large campus. The wireless network uses lightweight APs and multiple WLCs. A network technician walks around the campus to verify that wireless clients can roam smoothly between APs bound to different WLCs and assigned different VLANs and IP subnets. The technician verifies that while the client roams around campus, the client retains the same VLAN and IP address assigned. Which roaming scenario is the technician verifying?
- intracontroller roaming
- local-to-local roaming
- Layer 2 roaming
- Layer 3 roaming
26. A company deploys a Cisco wireless network over the campus. Wireless network access is needed for visitors to access the internet while on campus. What are two best practices in setting up APs and WLCs for secure wireless connections for visitors? (Choose two.)
- only using private IP addresses for APs and clients
- using static IP addressing for clients to better locate visitor clients
- putting the anchor controller specific for visitors behind firewall
- configuring a WLC to be a static anchor controller specific for visitors to associate
- deploying autonomous APs for visitors
27. What is a difficulty in locating a wireless client based on the RSS value when received by only one AP?
- The orientation where the client is situated in relation to the AP cannot be determined.
- The RSS value is affected by the air temperature.
- The distance from the client to the AP cannot be accurately determined.
- The RSS value is affected by moisture in the air.
28. Which two Cisco location solutions can work with Cisco management platforms to provide real-time location services for a wireless network? (Choose two.)
- Prime Infrastructure
- Mobility Services Engine
- DNA Space
- DNA Center
- Identity Services Engine
29. What is a Cisco solution developed to improve the results of wireless device location based on RSS values received by multiple APs?
- integrating customized GPS service on campus
- using DNA Center to provide secondary location parameters
- optimizing the algorithm to use 7 APs for determining the location
- developing RF fingerprinting where each mapped area is compensated with a calibration template
30. Which tunneling technology is used to facilitate data exchange between a lightweight AP and a WLAN controller?
- CAPWAP tunnel
- IPsec tunnel
- GRE tunnel
- overlay tunnel
31. Which technique is used by Cisco WLCs to minimize the time required on key exchanges during roaming by maintaining a database of clients and keys on behalf of bound APs, and providing those clients and keys to other controllers and bound APs as needed during roaming?
- Cisco Centralized Key Management (CCKM)
- intercontroller roaming
- key caching
- 802.11r support
32. How is wireless client location determined based on RSS values when using three or more APs?
- comparing the RSS values to choose the location of the AP with the highest RSS received
- correlating the RSS values received by multiple APs to determine where the LAN switches that are connected to the APs intersect
- correlating the RSS values received by multiple APs to determine where they intersect
- comparing the RSS values received by multiple APs to choose the shortest straight distance
33. What technology does a Cisco WLC use to provide Layer 3 roaming to a wireless client?
- a CAPWAP tunnel that tethers the client to the original anchor controller
- an IPsec tunnel to connect the client to the original AP
- a NAT translation to match the IP address in the roamed AP to the original AP
- a GRE tunnel to relay the data between the original AP and the roamed AP







